Speech Recognition (Library)¶
This example shows you a practical ASR example using ESPnet as a command line interface and library.
See also
run in colab
documetation https://espnet.github.io/espnet/
github https://github.com/espnet
Author: Shigeki Karita
Installation¶
ESPnet depends on Kaldi ASR toolkit and Warp-CTC. This cell will take a few minutes.
[ ]:
# TODO(karita): put these lines in ./espnet/tools/setup_colab.sh
# OS setup
!sudo apt-get install bc tree
!cat /etc/os-release
# espnet setup
!git clone https://github.com/espnet/espnet
!cd espnet; pip install -e .
!mkdir espnet/tools/venv/bin; touch espnet/tools/venv/bin/activate
# warp ctc setup
!git clone https://github.com/espnet/warp-ctc -b pytorch-1.1
!cd warp-ctc && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make -j4
!cd warp-ctc/pytorch_binding && python setup.py install
# kaldi setup
!cd ./espnet/tools; git clone https://github.com/kaldi-asr/kaldi
!echo "" > ./espnet/tools/kaldi/tools/extras/check_dependencies.sh # ignore check
!chmod +x ./espnet/tools/kaldi/tools/extras/check_dependencies.sh
!cd ./espnet/tools/kaldi/tools; make sph2pipe sclite
!rm -rf espnet/tools/kaldi/tools/python
![ ! -e ubuntu16-featbin.tar.gz ] && wget https://18-198329952-gh.circle-artifacts.com/0/home/circleci/repo/ubuntu16-featbin.tar.gz
!tar -xf ./ubuntu16-featbin.tar.gz
!cp featbin/* espnet/tools/kaldi/src/featbin/
ESPnet data preparation¶
You can use the end-to-end script run.sh for reproducing systems reported in espnet/egs/*/asr1/RESULTS.md. Typically, we organize run.sh with several stages:
Data download (if available)
Kaldi-style data preparation
Dump useful data for traning (e.g., JSON, HDF5, etc)
Lanuage model training
ASR model training
Decoding and evaluation
For example, if you add --stop-stage 2, you can stop the script before neural network training.
[ ]:
!cd espnet/egs/an4/asr1; ./run.sh --ngpu 1 --stop-stage 2
Kaldi-style directories¶
Always we organize each recipe placed in egs/xxx/asr1 in Kaldi way. For example, the important directories are:
conf/: kaldi configurations, e.g., speech featuredata/: almost raw data prepared by Kaldiexp/: intermidiate files through experiments, e.g., log files, model parametersfbank/: speech feature binary files, e.g., ark, scpdump/: ESPnet meta data for tranining, e.g., json, hdf5local/: corpus specific data preparation scripts
[ ]:
!tree -L 1
!ls data/train
.
├── espnet
├── featbin
├── sample_data
├── ubuntu16-featbin.tar.gz
└── warp-ctc
4 directories, 1 file
ls: cannot access 'data/train': No such file or directory
ESPnet as a library¶
Here we use ESPnet as a library to create a simple Python snippet for speech recognition. ESPnet ‘s training script’asr_train.py has three parts:
Load train/dev dataset
Create minibatches
Build neural networks
Update neural networks by iterating datasets
Let’s implement these procedures from scratch!
Load train/dev dataset (1/4)¶
First, we will check how run.sh organized the JSON files and load the pair of the speech feature and its transcription.
[2]:
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import kaldiio
root = "espnet/egs/an4/asr1"
with open(root + "/dump/train_nodev/deltafalse/data.json", "r") as f:
train_json = json.load(f)["utts"]
with open(root + "/dump/train_dev/deltafalse/data.json", "r") as f:
dev_json = json.load(f)["utts"]
# the first training data for speech recognition
key, info = next(iter(train_json.items()))
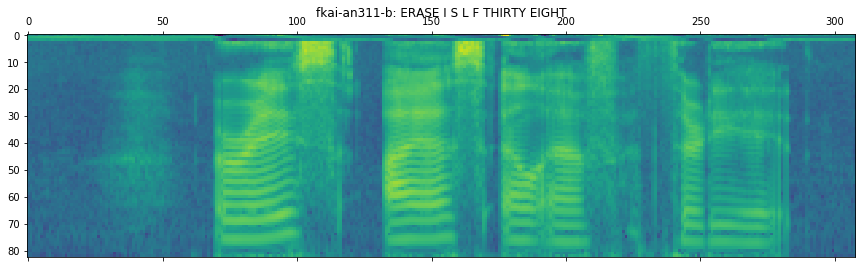
# plot the 80-dim fbank + 3-dim pitch speech feature
fbank = kaldiio.load_mat(info["input"][0]["feat"])
plt.matshow(fbank.T[::-1])
plt.title(key + ": " + info["output"][0]["text"])
# print the key-value pair
key, info
[2]:
('fkai-an311-b',
{'input': [{'feat': '/content/espnet/egs/an4/asr1/dump/train_nodev/deltafalse/feats.1.ark:13',
'name': 'input1',
'shape': [308, 83]}],
'output': [{'name': 'target1',
'shape': [26, 30],
'text': 'ERASE I S L F THIRTY EIGHT',
'token': 'E R A S E <space> I <space> S <space> L <space> F <space> T H I R T Y <space> E I G H T',
'tokenid': '7 20 3 21 7 2 11 2 21 2 14 2 8 2 22 10 11 20 22 27 2 7 11 9 10 22'}],
'utt2spk': 'fkai'})
Create minibatches (2/4)¶
To parallelize neural network training, we create minibatches that containes several sequence pairs by splitting datasets.
[3]:
from espnet.utils.training.batchfy import make_batchset
batch_size = 32
trainset = make_batchset(train_json, batch_size)
devset = make_batchset(dev_json, batch_size)
assert len(devset[0]) == batch_size
devset[0][:3]
[3]:
[('fbbh-an89-b',
{'input': [{'feat': '/content/espnet/egs/an4/asr1/dump/train_dev/deltafalse/feats.1.ark:257878',
'name': 'input1',
'shape': [638, 83]}],
'output': [{'name': 'target1',
'shape': [40, 30],
'text': 'RUBOUT T G J W B SEVENTY NINE FIFTY NINE',
'token': 'R U B O U T <space> T <space> G <space> J <space> W <space> B <space> S E V E N T Y <space> N I N E <space> F I F T Y <space> N I N E',
'tokenid': '20 23 4 17 23 22 2 22 2 9 2 12 2 25 2 4 2 21 7 24 7 16 22 27 2 16 11 16 7 2 8 11 8 22 27 2 16 11 16 7'}],
'utt2spk': 'fbbh'}),
('fejs-cen4-b',
{'input': [{'feat': '/content/espnet/egs/an4/asr1/dump/train_dev/deltafalse/feats.4.ark:106716',
'name': 'input1',
'shape': [528, 83]}],
'output': [{'name': 'target1',
'shape': [23, 30],
'text': 'F I N D L E Y D R I V E',
'token': 'F <space> I <space> N <space> D <space> L <space> E <space> Y <space> D <space> R <space> I <space> V <space> E',
'tokenid': '8 2 11 2 16 2 6 2 14 2 7 2 27 2 6 2 20 2 11 2 24 2 7'}],
'utt2spk': 'fejs'}),
('ffmm-cen2-b',
{'input': [{'feat': '/content/espnet/egs/an4/asr1/dump/train_dev/deltafalse/feats.5.ark:52535',
'name': 'input1',
'shape': [498, 83]}],
'output': [{'name': 'target1',
'shape': [21, 30],
'text': 'F R A N C E S M A R Y',
'token': 'F <space> R <space> A <space> N <space> C <space> E <space> S <space> M <space> A <space> R <space> Y',
'tokenid': '8 2 20 2 3 2 16 2 5 2 7 2 21 2 15 2 3 2 20 2 27'}],
'utt2spk': 'ffmm'})]
Build neural networks (3/4)¶
For simplicity, we use a predefined model: Transformer.
NOTE: You can also use your custom model in command line tools as asr_train.py --model-module your_module:YourModel
[5]:
import argparse
from espnet.bin.asr_train import get_parser
from espnet.nets.pytorch_backend.e2e_asr import E2E
parser = get_parser()
parser = E2E.add_arguments(parser)
config = parser.parse_args([
"--mtlalpha", "0.0", # weight for cross entropy and CTC loss
"--outdir", "out", "--dict", ""]) # TODO: allow no arg
idim = info["input"][0]["shape"][1]
odim = info["output"][0]["shape"][1]
setattr(config, "char_list", [])
model = E2E(idim, odim, config)
model
[5]:
E2E(
(enc): Encoder(
(enc): ModuleList(
(0): RNNP(
(birnn0): LSTM(83, 300, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
(bt0): Linear(in_features=600, out_features=320, bias=True)
(birnn1): LSTM(320, 300, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
(bt1): Linear(in_features=600, out_features=320, bias=True)
(birnn2): LSTM(320, 300, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
(bt2): Linear(in_features=600, out_features=320, bias=True)
(birnn3): LSTM(320, 300, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
(bt3): Linear(in_features=600, out_features=320, bias=True)
)
)
)
(ctc): CTC(
(ctc_lo): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=30, bias=True)
(ctc_loss): CTCLoss()
)
(att): ModuleList(
(0): AttDot(
(mlp_enc): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=320, bias=True)
(mlp_dec): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=320, bias=True)
)
)
(dec): Decoder(
(embed): Embedding(30, 320)
(dropout_emb): Dropout(p=0.0)
(decoder): ModuleList(
(0): LSTMCell(640, 320)
)
(dropout_dec): ModuleList(
(0): Dropout(p=0.0)
)
(output): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=30, bias=True)
(att): ModuleList(
(0): AttDot(
(mlp_enc): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=320, bias=True)
(mlp_dec): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=320, bias=True)
)
)
)
)
Update neural networks by iterating datasets (4/4)¶
Finaly, we got the training part.
[7]:
import numpy
import torch
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence
from torch.nn.utils.clip_grad import clip_grad_norm_
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
def collate(minibatch):
fbanks = []
tokens = []
for key, info in minibatch[0]:
fbanks.append(torch.tensor(kaldiio.load_mat(info["input"][0]["feat"])))
tokens.append(torch.tensor([int(s) for s in info["output"][0]["tokenid"].split()]))
ilens = torch.tensor([x.shape[0] for x in fbanks])
return pad_sequence(fbanks, batch_first=True), ilens, pad_sequence(tokens, batch_first=True)
train_loader = DataLoader(trainset, collate_fn=collate, shuffle=True, pin_memory=True)
dev_loader = DataLoader(devset, collate_fn=collate, pin_memory=True)
model.cuda()
optim = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.98))
n_iter = len(trainset)
n_epoch = 10
total_iter = n_iter * n_epoch
train_acc = []
valid_acc = []
for epoch in range(n_epoch):
# training
acc = []
model.train()
for data in train_loader:
loss = model(*[d.cuda() for d in data])
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
acc.append(model.acc)
norm = clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 10.0)
optim.step()
train_acc.append(numpy.mean(acc))
# validation
acc = []
model.eval()
for data in dev_loader:
model(*[d.cuda() for d in data])
acc.append(model.acc)
valid_acc.append(numpy.mean(acc))
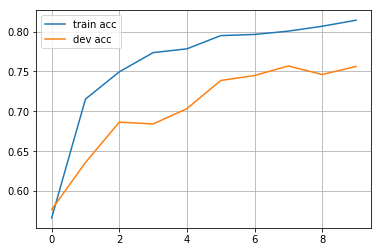
print(f"epoch: {epoch}, train acc: {train_acc[-1]:.3f}, dev acc: {valid_acc[-1]:.3f}")
epoch: 0, train acc: 0.566, dev acc: 0.577
epoch: 1, train acc: 0.715, dev acc: 0.636
epoch: 2, train acc: 0.750, dev acc: 0.686
epoch: 3, train acc: 0.774, dev acc: 0.684
epoch: 4, train acc: 0.778, dev acc: 0.703
epoch: 5, train acc: 0.795, dev acc: 0.739
epoch: 6, train acc: 0.796, dev acc: 0.745
epoch: 7, train acc: 0.801, dev acc: 0.757
epoch: 8, train acc: 0.807, dev acc: 0.746
epoch: 9, train acc: 0.814, dev acc: 0.756
[8]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(len(train_acc)), train_acc, label="train acc")
plt.plot(range(len(valid_acc)), valid_acc, label="dev acc")
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
[8]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f76f9c22a20>
[ ]:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "best.pt")
Recognize speech¶
[16]:
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import kaldiio
from espnet.bin.asr_recog import get_parser
# load data
root = "espnet/egs/an4/asr1"
with open(root + "/dump/test/deltafalse/data.json", "r") as f:
test_json = json.load(f)["utts"]
key, info = list(test_json.items())[10]
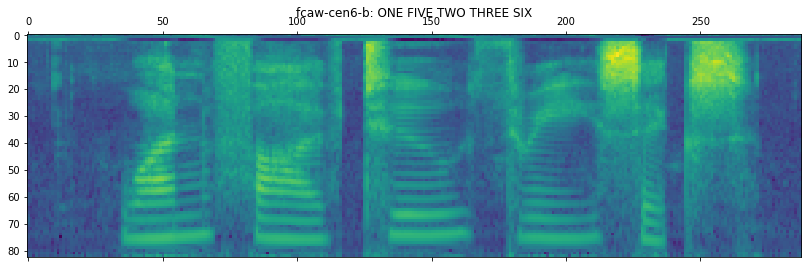
# plot the 80-dim fbank + 3-dim pitch speech feature
fbank = kaldiio.load_mat(info["input"][0]["feat"])
plt.matshow(fbank.T[::-1])
plt.title(key + ": " + info["output"][0]["text"])
# load token dict
with open(root + "/data/lang_1char/train_nodev_units.txt", "r") as f:
token_list = [entry.split()[0] for entry in f]
token_list.insert(0, '<blank>')
token_list.append('<eos>')
# recognize speech
parser = get_parser()
args = parser.parse_args([
"--beam-size", "1",
"--ctc-weight", "0",
"--result-label", "out.json",
"--model", ""
])
model.cpu()
model.eval()
def to_str(result):
return "".join(token_list[y] for y in result[0]["yseq"]) \
.replace("<eos>", "").replace("<space>", " ").replace("<blank>", "")
print("groundtruth:", info["output"][0]["text"])
print("prediction: ", to_str(model.recognize(fbank, args, token_list)))
groundtruth: ONE FIVE TWO THREE SIX
prediction: ONE FIVE TWO ONE THREE TWO ONE THREE
[ ]: